Novel Coronavirus 2019 – The Comprehensive Guide to COVID-19
This handy infographic is a quick reference guide to understanding all about the COVID-19 virus including symptoms, how it transmits, how to prevent getting the virus, and what to do should you get it.
COVID-19 Epidemiology – Origin
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are common in many different species of animals, including camels, cattle, cats, and bats. Rarely, animal coronaviruses can infect people and then spread between people.
The sequences from U.S. patients are similar to the one that China initially posted, suggesting a likely single, recent emergence of this virus from an animal reservoir.
Early on, many of the patients in the COVID-19 outbreak in Wuhan, China, had some link to a seafood and live animal market, suggesting animal-to-person spread. Later, a growing number of patients reportedly did not have exposure to animal markets, indicating person-to-person spread.
Experts have reported person-to-person transmission outside China, including in the United States; Canada, Mexico, Europe (Italy, France, Germany, Spain, Switzerland), Asia (South Korea, Japan, Singapore), and other locations. Chinese officials report that sustained person-to-person spread in the community is occurring in China.
Additionally, other destinations have apparent community spread. Community-spread means some infected people are not sure how or where they became infected. Learn what is known about the dispersion of newly emerged coronaviruses
Transmission – How Does COVID-19 Spread & Sources of Transmission
How COVID-19 Spreads
Current understanding about how the Novel Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) spreads is based mainly on known coronaviruses. COVID-19 is a new disease, and there is more to learn about how it transmits, the severity of illness it causes, and to what extent it may spread in the United States.
- Person-to-person transmission
- Between people who are in close contact with one another (within about 6 feet, through respiratory droplets produced when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- These droplets can land in the mouths or noses of people who are nearby or possibly inhaled into the lungs.
- Spread from contact with infected surfaces or objects
- It may be possible that a person can get COVID-19 by touching a surface or object that has the virus on it and then touching their mouth, nose, or possibly their eyes. However, experts do not believe this to be the primary way the virus spreads.
Can Someone Spread the COVID-19 Virus Without Being Sick?
Experts suspect people are most contagious when they are symptomatic.
Contamination can occur before people show symptoms. There have been reports of this happening with this new coronavirus, but this is not thought to be the central way the virus spreads.
How Easily Does COVID-19 Spread?
How easily a virus spreads from person-to-person can vary. Some illnesses are highly contagious (spread quickly).
The virus that causes COVID-19 seems to be spreading swiftly and sustainably in the community (“community spread”) in some affected geographic areas. Community-Spread means infected individuals with the virus in a region transmit the virus from person-to-person, including those uncertain how or where they became infected.
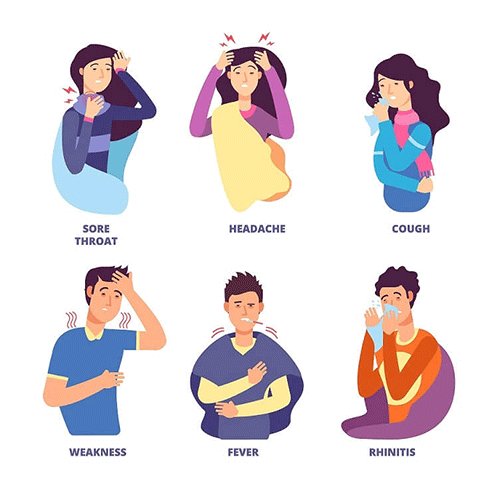
For determined Novel Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) cases, reported illnesses have ranged from mild symptoms to severe infection, up to and including death. Symptoms can include:
- Fever
- Cough
- Shortness of breath
The CDC believes at this time that symptoms of COVID-19 may appear in as few as two (2) days with the possibility of showing over 14+ days after exposure. This is based on what has been seen previously as the incubation period of MERS-CoV viruses.
The latest situation summary updates are available on the CDC’s coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) web page.
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/about/transmission.html
What to do if you or Someone is Suspected of Having COVID-19?
 Prevention of COVID-19
Prevention of COVID-19
There is currently no vaccine to prevent novel coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). The best way to prevent illness is to avoid exposure to the virus.
However, as a reminder, the CDC always recommends everyday preventive actions to help prevent the spread of respiratory diseases, including:
- Avoid close contact with people who are sick.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Stay home when you are sick.
- Cover your cough or sneeze with a tissue, then throw the tissue in the trash.
- Clean and disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces using a regular household cleaning spray or wipe.
- Follow CDC’s recommendations for using a facemask.
- CDC does not recommend that people who are well to wear a facemask to protect themselves from respiratory diseases, including COVID-19.
- Facemasks should be used by people who show symptoms of COVID-19 to help prevent the spread of the disease to others. The use of facemasks is also crucial for health workers and people who are taking care of someone in close settings (at home or in a health care facility).
- Wash your hands often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after going to the bathroom; before eating; and after blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing.
- If soap and water are not readily available, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol. Always wash hands with soap and water if hands are visibly dirty.
For information about handwashing, see CDC’s Handwashing website
For information specific to healthcare, see CDC’s Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings
These are everyday habits that can help prevent the spread of several viruses. CDC does have guidance for travelers.
What to do if the Novel Coronavirus 2019 is Confirmed
-
- You should restrict activities outside your home, except for getting medical care.
- Do not go to work, school, or public areas.
- Avoid using public transportation, ridesharing, or taxis.
- Separate yourself from other people and animals in your home: you should stay in a specific room and away from other people in your home.
- Also, you should use a separate bathroom, if available.
- Call ahead before visiting your doctor If you have a medical appointment, call the healthcare provider and tell them that you have or may have COVID-19. Calling ahead will help the healthcare provider’s office take steps to keep other people from getting infected or exposed.
- Wear a facemask. You should wear a facemask when you are around other people (e.g., sharing a room or vehicle) or pets and before you enter a healthcare provider’s office.
- If you are not able to wear a facemask (for example, because it causes trouble breathing), then people who live with you should not stay in the same room with you, or they should wear a facemask if they enter your room.
- Cover your coughs and sneezes. Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze. Throw used tissues in a lined trash can. Immediately wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. It’s helpful to remember 20 seconds is equivalent to singing Row, Row your Boat” three times, or “Happy Birthday” twice. A second-best option is to clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand sanitizer that contains at least 60 to 95% alcohol, covering all surfaces of your hands and rubbing them together until they feel dry. Use soap and water instead of a hand sanitizer if your hands are visibly dirty.
- Avoid sharing personal household items. You should not share dishes, drinking glasses, cups, eating utensils, towels, or bedding with other people or pets in your home. After using these items, they should be washed thoroughly with soap and water.
Key Contacts (CDC, WHO, San Francisco Department of Public Health)
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/index.html
https://www.who.int/health-topics/coronavirus
https://www.sfdph.org/dph/
Any other Key Pieces of Information not contained in these Subsets (Health Map of the Coronavirus Outbreak)
https://healthmap.org/covid-19/
https://www.nejm.org/coronavirus





Comment(1)